For selection of IKO CRW series crossed roller way guides specifications, stroke length and the number of cylindrical rollers, as well as accuracy, load rating and allowable load, must be determined.
Stroke length and the number of cylindrical rollers
Stroke length of IKO CRW crossed roller way guides affects the way length and the number of cylindrical rollers. Therefore, select specifications by following the procedure below taking into account the stroke length used and applied load.
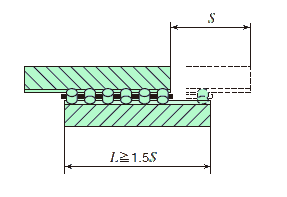
1, Calculation of way length
The way length, which should be 1.5 times longer than the stroke length used, is obtained from the equation below.
Where,
L: Way length mm
S: Stroke length used mm
2, Calculation of maximum stroke length
Ideally the stroke length used should be less than 80% of the maximum stroke length, which is obtained from the equation below.
Where,
S1: Maximum stroke length mm
S: Stroke length used mm
3, Calculation of cage length and the number of rollers
With the way length and maximum stroke length determined, the allowable length for cage can be calculated.
Calculation method of the cage length varies depending on specifications of end screws and end stopper fitted to the way end.
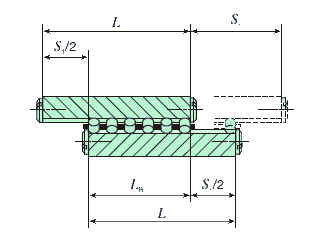
(1) With standard end screws and end stopper SA (excluding Size 1 series)
The dimensions between rollers at both ends is obtained from the following equation by using a value obtained by subtracting a half of the maximum stroke length from the way length.
Where,
LR: Allowable dimensions between rollers at both ends mm
L: Way length mm
S1: Maximum stroke length mm
The number of rollers to be incorporated in a roller cage is obtained by the following equation.
Where,
Z: Number of cylindrical rollers (figures after the decimal fractions are omitted)
LR: Allowed dimensions between rollers at both ends mm
DW: Diameter of cylindrical rollers (refer to the dimension table) mm
P: Inter-pitch dimensions of cylindrical rollers (refer to the dimension table) mm
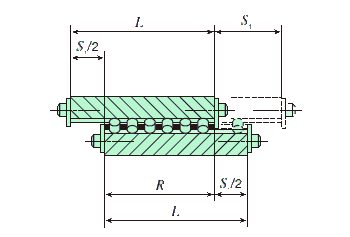
(2) For Size 1 series
The stroke length is regulated by cage and end stopper and the cage length is obtained by the following equation.
Where,
R: Allowable cage length mm
L: Way length mm
S1: Maximum stroke length mm
The number of rollers to be incorporated in a roller cage is obtained by the following equation.
Where,
Z: Number of cylindrical rollers (figures after the decimal fractions are omitted)
R: Allowable cage length mm
e: End dimension of cage (refer to the dimension table) mm
p: Inter-pitch dimensions of cylindrical rollers (refer to the dimension table) mm
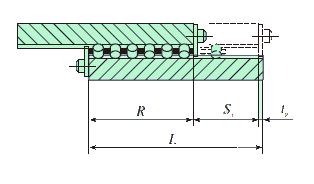
(3) For end stopper SB and wiper seal
The stroke length is regulated by cage and end stopper or wiper seal and the cage length is obtained by the following equation.
Where,
R: Allowable cage length mm
L: Way length mm
S1: Maximum stroke length mm
t2: Thickness of end stopper SB or wiper seal mm
The number of rollers to be incorporated in a roller cage is obtained by the equation as with the Size 1 series.
Calculation examples
Model
CRW 6
Applies load
P = 7000 N
Stroke length
S = 195 mm
Select specifications for parallel use of Crossed Roller Way under the above conditions
Calculation of way length
Therefore, select L = 300 mm based on the standard length in the dimension table.
Calculation of maximum stroke length
The maximum stroke length S1
Allowable dimensions between rollers at both ends LR
Calculation of the number of rollers
Therefore, it should be Z = 20 by omitting figures after the decimal fractions.
Calculation of allowable load
Allowable load in parallel arrangement F is calculated as follow (please refer to allowable load. However, allowable load per cylindrical roller Fu is Fu = 769 N according to the dimension table.
Therefore, allowable load F is larger than applied load P = 7000 N. When allowable load becomes smaller than applied load, it is necessary to increase the number of cylindrical rollers by extending way length, or increase the cylindrical roller diameter.
Determination of specifications
Specifications obtained in accordance with the above is CRW6-300 and the number of cylindrical rollers is 20.
