A bearing arrangement supports and locates a shaft, radially and axially, relative to other components such as housings. Typically, two bearing supports are required to position a shaft. Depending on certain requirements, such as stiffness or load directions, a bearing support may consist of one or more bearings.
When considering the bearing arrangement, the following items must be investigated:
- Expansion and contraction of the shaft caused by temperature variations.
- Ease of bearing mounting and dismounting.
- Misalignment of the inner and outer rings caused by deflection of the shaft or mounting error.
- Rigidity of the entire system including bearings and preloading method.
- Capability to sustain the loads at their proper positions and to transmit them.
The bearing which prevents axial movement of the shaft relative to the housing is called the "fixed side bearing" and the bearing which allows axial movement relatively is called the "floating-side bearing". This allows for expansion and contraction of the shaft due to temperature variation and enables error in bearing mounting clearance to be absorbed.
The fixed side bearing is able to support radial and axial loads. A bearing which can fix axial movement in both directions should therefore be selected. A floatingside bearing that allows movement in the axial direction while supporting a radial load is desirable. Movement in the axial direction occurs on the raceway surface for bearings with separable inner and outer rings such as cylindrical roller bearings, and occurs on the fitting surface for those which are not separable, such as deep groove ball bearings.
In applications with short distances between bearings, shaft expansion and contraction due to temperature fluctuations is slight, therefore the same type of bearing may be used for both the fixed-side and floating-side bearing. In such cases it is common to use a set of matching bearings, such as angular contact ball bearings, to guide and support the shaft in one axial direction only.
Table below shows typical bearing arrangements where the bearing type differs on the fixed side and floating side.
| Arrangement | Comment | Application (Reference) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed | Floating | ||
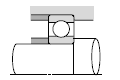 | 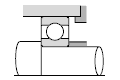 |
| Small pumps, auto-mobile transmissions, etc. |
 | 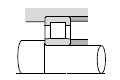 |
| Medium-sized electric motors, ventilators, etc. |
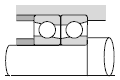 | 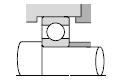 |
| Worm reduction gear |
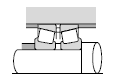 |  |
| Reduction gears for general industrial machinery |
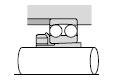 | 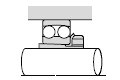 |
| General industrial machinery |
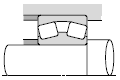 | 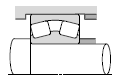 |
| Reduction gears for general industrial machinery |
 |  |
| Reduction gears for general industrial machinery |
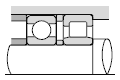 |  |
| Transmissions for diesel locomotives |
Table below shows some common bearing arrangements where no distinction is made between the fixed side and floating side.
| Arrangement | Comment | Application (Reference) |
|---|---|---|
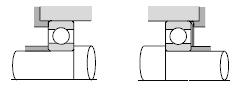 |
| Small electric motors, small reduction gears, etc. |
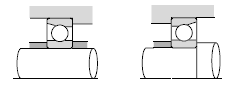 |
| Machine tool spindles, etc. |
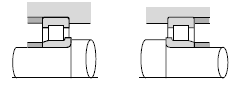 |
| Construction equipment, mining equipment sheaves, agitators, etc. |
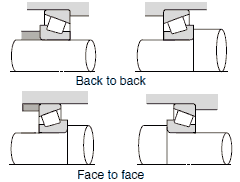 |
| Reduction gears, front and rear axle of automobiles, etc. |
Vertical shaft bearing arrangements are shown in Table below
| Arrangement | Comment | Application (Reference) |
|---|---|---|
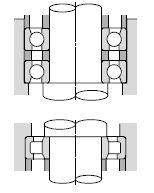 |
| Vertically mounted electric motors, etc. |
 |
| Crane center shafts, etc. |
